How To Update Certificates On Windows 10
All Windows versions have a born feature for automatically updating root certificates from the Microsoft websites. MSFT, as part of the Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program, maintains and publishes a list of trusted certificates for clients and Windows devices in its online repository. If the verified document in its certification concatenation refers to the root CA that participates in this program, the system volition automatically download this root certificate from the Windows Update servers and add it to the trusted ones.
Windows updates a trusted root certificate list (CTL) once a calendar week. If Windows doesn't take directly admission to the Windows Update, the system won't exist able to update the root certificates. So a user may take some troubles when browsing websites (which SSL certificates are signed past an untrusted CA – see the article almost the "Chrome SSL error: This site can't provide a secure connexion"), or with installing/running signed scripts and apps.
In this article, we'll attempt to observe out how to manually update the list of root certificates in TrustedRootCA in disconnected (isolated) networks or computers/servers without direct Net access.
Contents:
- Managing Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10 and 11
- How to Disable/Enable Automatic Root Certificates Update in Windows?
- Certutil: Download Trusted Root Certificates from Windows Update
- Certificate Trust List (STL) in Windows
- Updating Trusted Root Certificates via GPO in an Isolated Environment
- How to Update Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 7?
- Updating Root Certificates on Windows XP Using the Rootsupd.exe Tool
Note. If your computers access the Internet through a proxy server, Microsoft recommends that you open direct admission (bypass) to Microsoft Spider web sites to automatically renew root certificates. Nevertheless, it isn't always possible or applicable due to corporate restrictions.
Managing Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10 and 11
How to run into the listing of trusted root certificates on a Windows computer?
- To open up the root certificate store of a computer running Windows 11/10/eight.1/seven or Windows Server 2022/2019/2016, run the mmc.exe console;
- Select File -> Add/Remove Snap-in, select Certificates (certmgr) in the list of snap-ins -> Add together;
- Select that you desire to manage certificates of local Computer business relationship;
- Side by side -> OK -> OK;
- Expand the Certificates node -> Trusted Root Certification Government Shop. This department contains the list of trusted root certificates on your reckoner.
In the mmc console, you can view information about whatever certificate or remove it from trusted ones.
Y'all can also go a listing of trusted root certificates with their expiration dates using PowerShell:
Go-Childitem cert:\LocalMachine\root |format-list
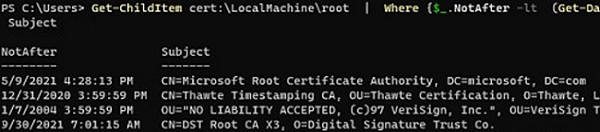
Yous can listing the expired certificates, or which expire in the next 60 days:
Become-ChildItem cert:\LocalMachine\root|Where {$_.NotAfter -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(sixty)}|select NotAfter, Field of study
For security reasons, it's recommended that you periodically bank check the certificate trust store on your calculator for suspicious and revoked certificates using the Sigcheck tool. This tool allows you lot to compare the list of certificates installed on the computer with the list of root certificates on the Microsoft website (you can download an offline file with upwards-to-date certificates authrootstl.cab).
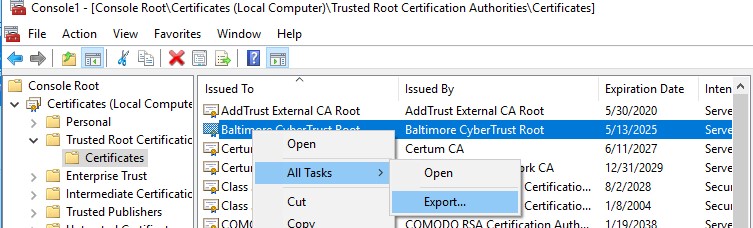
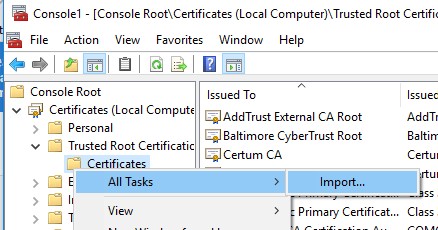
You can manually transfer the root certificate file betwixt Windows computers using the Export/Import options.
- You can export whatsoever certificate to a .CER file by clicking on it and selecting All Tasks -> Consign;
- You can import this certificate on some other computer using the selection All Tasks -> Import.
How to Disable/Enable Automatic Root Certificates Update in Windows?
As we mentioned, Windows automatically updates root certificates. You tin enable or disable certificate renewal in Windows through a GPO or the registry.
Open the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) and go to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Organization -> Internet Advice Management -> Net Communication.
The Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update choice in this section allows you to disable automated updating of root certificates through the Windows Update sites. By default, this policy is not configured and Windows ever tries to automatically renew root certificates.
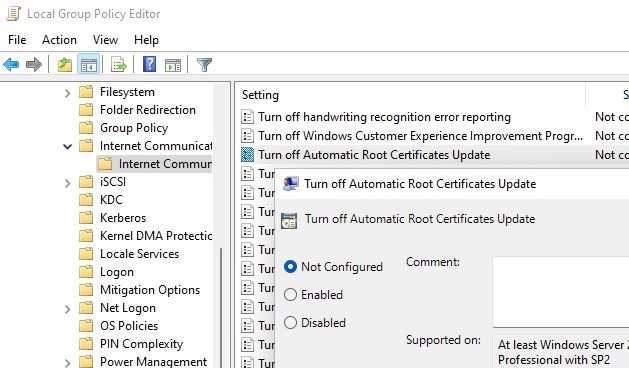
If this GPO option is non configured and the root certificates are not automatically renewed, check if this setting is manually enabled in the registry. Check the value of the registry parameter using PowerShell:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot' -Name DisableRootAutoUpdate
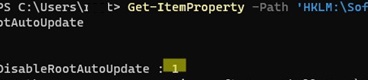
If the command returns that the value of the DisableRootAutoUpdate registry parameter is one, and then the updating of root certificates is disabled on your estimator. To enable it, change the parameter value to 0.
Certutil: Download Trusted Root Certificates from Windows Update
Certutil.exe CLI tool can exist used to manage certificates (introduced in Windows 10, for Windows 7 is available every bit a split up update). Information technology tin can exist used to download an upwardly-to-date list of root certificates from Windows Update and save it to an SST file.
To generate an SST file on a computer running Windows x or xi and having direct access to the Cyberspace, open up the elevated command prompt and run the command:
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU C:\PS\roots.sst
Updated SST file. CertUtil: -generateSSTFromWU command completed successfully.
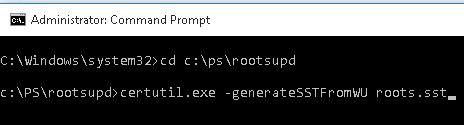
As a result, an SST file containing an upwardly-to-date list of root certificates will appear in the target directory. Double-click to open it. This file is a container containing trusted root certificates.
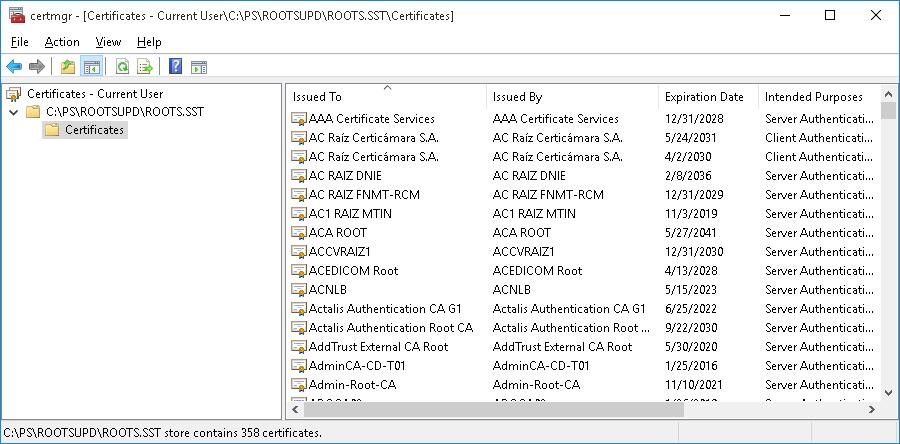
As you can see, a familiar Document Management snap-in opens, from which y'all can export whatsoever of the certificates y'all take got. In my case, in that location take been 358 items in the listing of certificates. Plain, information technology is not rational to export the certificates and install them one by i.
Tip. The certutil -syncWithWU command tin can be used to generate individual document files. The certificates obtained in this way tin can be deployed to Windows devices using GPO.
You can use PowerShell script to install all certificates from the SST file and add them to the list of trusted root certificates on a estimator:
$sstStore = ( Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ps\rootsupd\roots.sst )
$sstStore | Import-Document -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
Run the certmgr.msc snap-in and brand certain that all certificates take been added to the Trusted Root Certification Authorisation. In my case on Windows 11, the number of root certificates increased from 34 to 438.
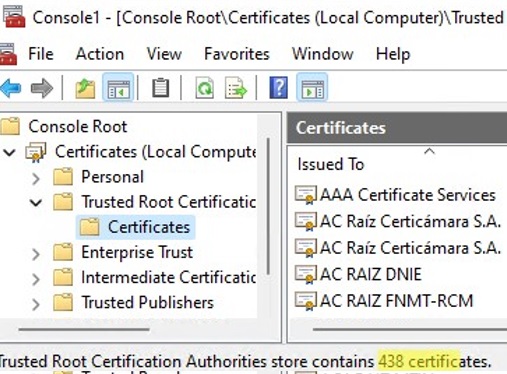
A clean re-create of Windows later on installation contains only a small number of certificates in the root store. If the computer is connected to the Internet, the rest of the root certificates will be installed automatically (on demand) if your device access an HTTPS site or SSL certificate that has a fingerprint from Microsoft CTL in its trust chain. Therefore, equally a rule, there is no need to immediately add together all certificates that Microsoft trusts to the local certification store.
Certificate Trust List (STL) in Windows
A Document Trust List (CTL) is simply a list of information (such as document hashes) that is signed by a trusted party (by Microsoft in this case). The Windows client periodically downloads from Windows Update this CTL, which stores the hashes of all trusted root CAs. It should be understood that this CTL doesn't comprise the certificates themselves, merely their hashes and attributes (for case, Friendly Name). Windows devices tin download a trusted certificate from Certificate Trust List on demand.
You tin manually download and install the CTL file. To do it, download the file http://ctldl.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/authrootstl.cab (updated twice a month). Using whatsoever archiver (or fifty-fifty Windows Explorer), unpack the contents of the authrootstl.cab annal. Information technology contains a single authroot.stl file.

The Authroot.stl file is a container with a list of trusted certificate thumbprints in Document Trust List format.
You lot tin can install this CTL file to a Trusted Root Certificate Dominance using the certutil command:
certutil -enterprise -f -5 -AddStore "Root" "C:\PS\authroot.stl"

root "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" CTL 0 added to store. CertUtil: -addstore control completed successfully.
You tin can as well import certificates using the certificate management panel (Trust Root Certification Regime -> Certificates -> All Tasks -> Import). Specify the path to your STL file with document thumbprints.
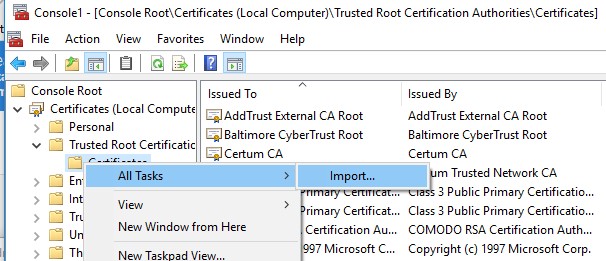
Afterward you have run the command, a new department Document Trust List appears in Trusted Root Certification Authorities container of the Certificate Manager console (certmgr.msc).
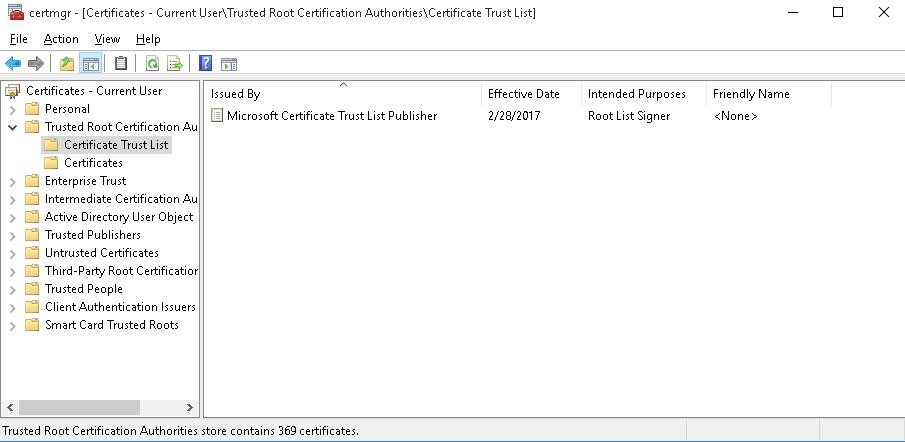
In the same fashion, you can download and install the list of the revoked (disallowed) certificates that have been removed from the Root Certificate Plan. To exercise it, download the disallowedcertstl.cab file (http://ctldl.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/disallowedcertstl.cab), excerpt it, and add information technology to the Untrusted Certificates store with the command:
certutil -enterprise -f -v -AddStore disallowed "C:\PS\disallowedcert.stl"
Updating Trusted Root Certificates via GPO in an Isolated Environment
If you lot have the chore of regularly updating root certificates in an Cyberspace-isolated Active Directory domain, there is a slightly more than complicated scheme for updating local document stores on domain-joined computers using Group Policies. Yous can configure root certificate updates on user computers in the disconnected Windows networks in several ways.
The start way assumes that you lot regularly manually download and copy a file with root certificates to your isolated network. You lot can download the file with current Microsoft root certificates as follows:
certutil.exe –generateSSTFromWU roots.sst
And then the root certificates from this file tin be deployed via SCCM or PowerShell Startup script in GPO:
$sstStore = (Get-ChildItem -Path \\fr-dc01\SYSVOL\woshub.com\rootcert\roots.sst )
$sstStore | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
The 2nd way is to download the bodily Microsoft root certificates using the control:
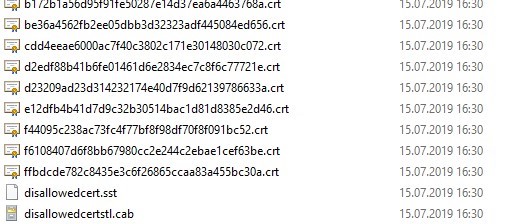
Certutil -syncWithWU -f \\fr-dc01\SYSVOL\woshub.com\rootcert\
A number of root certificate files (CRT file format) will appear in the specified shared network folder (including files authrootstl.cab, disallowedcertstl.cab, disallowedcert.sst, thumbprint.crt).
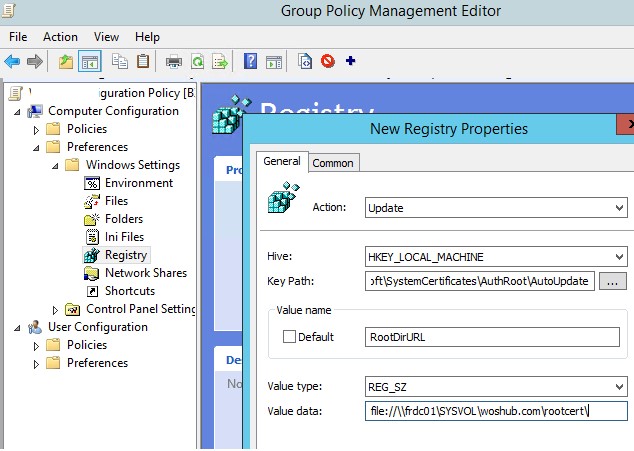
Then use the Group Policy Preferences to change the value of the registry parameter RootDirURLunder HKLM\Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot\AutoUpdate. This parameter should indicate to the shared network binder from which your Windows computers will receive new root certificates. Run the domain GPMC.msc console, create a new GPO, switch to the edit policy mode, and expand the section Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry. Create a new registry property with the following settings:
- Activity: Update
- Hive: HKLM
- Fundamental path: Software\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot\AutoUpdate
- Value name: RootDirURL
- Blazon: REG_SZ
- Value data: file://\\fr-dc01\SYSVOL\woshub.com\rootcert\
It remains to link this policy on a computer`s OU and after updating GPO settings on the customer, check for new root certificates in the certstore.
The GPO parameter Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update nether Reckoner Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Internet Communication Management -> Internet Communication settings should be disabled or not configured.
How to Update Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 7?
Despite the fact that Windows 7 is now is at the End of Support phase, many users and companies all the same use it.
Subsequently installing a clean Windows 7 image, yous may discover that many modern programs and tools do not work on it every bit they are signed with new certificates. In item, there have been complaints that .Cyberspace Framework 4.viii or Microsoft Visual Studio (vs_Community.exe) cannot be installed on Windows vii SP1 x64 without updating root certificates.
The installer manifest failed signature validation.
Or
NET Framework has not been installed because a certificate chain could not exist congenital to a trusted root authorisation.
To update root certificates in Windows vii, you must first download and install MSU update KB2813430 (https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/an-update-is-available-that-enables-administrators-to-update-trusted-and-disallowed-ctls-in-disconnected-environments-in-windows-0c51c702-fdcc-f6be-7089-4585fad729d6)
Afterwards that, you lot can employ the certutil to generate an SST file with root certificates (on current or some other computer):
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU c:\ps\roots.sst
Now you can import certificates into trusted ones:
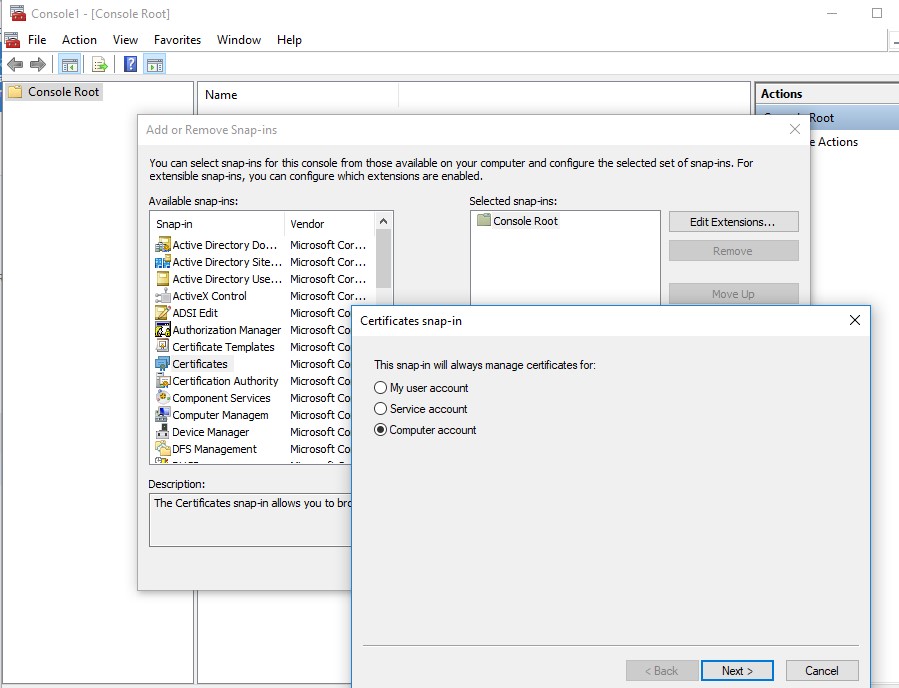
Run MMC -> add together snap-in -> certificates -> computer account > local computer. Right click Trusted root certification say-so, All Tasks -> Import, notice your SST file (in the file type select Microsoft Serialized Certificate Store — *.sst) -> Open up -> Identify all certificates in the following shop -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Updating Root Certificates on Windows XP Using the Rootsupd.exe Tool
In Windows XP, the rootsupd.exe utility was used to update the computer`s root certificates. The listing of root and revoked certificates in it was regularly updated. The tool was distributed as a carve up update KB931125 (Update for Root Certificates). Allow'due south see if we can use information technology now.
- Download the rootsupd.exe utility using the following link
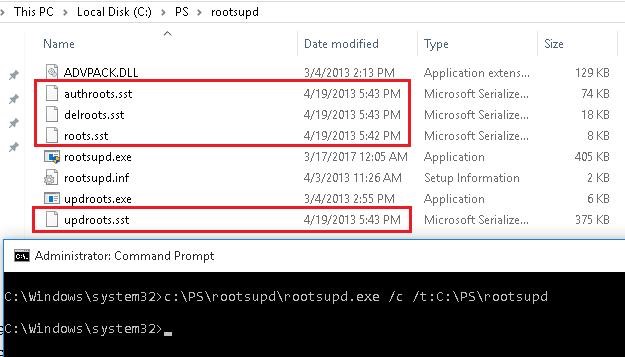
http://download.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/rootsupd.exe. At the moment (Jan 2021) the link doesn't work, Microsoft decided to remove it from the public. Today you can download the rootsupd.exe from the Kaspersky website — http://media.kaspersky.com/utilities/CorporateUtilities/rootsupd.zip; - To install the Windows root certificates, but run the rootsupd.exe file. But we will endeavor to examine its contents more carefully. Extract the certificates from the executable file with the command:
rootsupd.exe /c /t: C:\PS\rootsupd - Certificates are stored in SST files, similar authroots.sst, delroot.sst, etc. To remove or install certificates, you can utilize the post-obit commands:
updroots.exe authroots.sst
updroots.exe -d delroots.sst
Yet, equally you tin meet, these certificate files were created on April 4, 2013 (nearly a year before the stop of official support for Windows XP). Thus, since and then the tool has not been updated and cannot be used to install up-to-date certificates.
But yous tin utilise cerutil tool in Windows ten/11 to download root.sst, copy that file in Windows XP and install the document using updroots.exe:
updroots.exe c:\temp\roots.sst
There is information that the updroots.exe tool is not recommended for apply in modernistic builds of Windows 10 1803+ and Windows 11, as information technology tin break the Microsoft root CA on a device.
In this commodity, nosotros looked at several ways to update trusted root certificates on Windows network computers that are isolated from the Internet (disconnected environment).
Source: http://woshub.com/updating-trusted-root-certificates-in-windows-10/
Posted by: steelplam1994.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Update Certificates On Windows 10"
Post a Comment